In-Situ Orientation Search
In a system containing multiple molecules, it is useful to determine the most stable orientation of a target molecule relative to other molecules to analyze the interactions between solutes and solvents in a solution or between biopolymers and small ligand molecules.
CONFLEX has a function called “In-Situ Orientation Search”, which rotates the target molecule sequentially at the position of the input data to generate initial geometries, and then the energy-minimum complex structures with different orientations can be obtained by optimizing them.
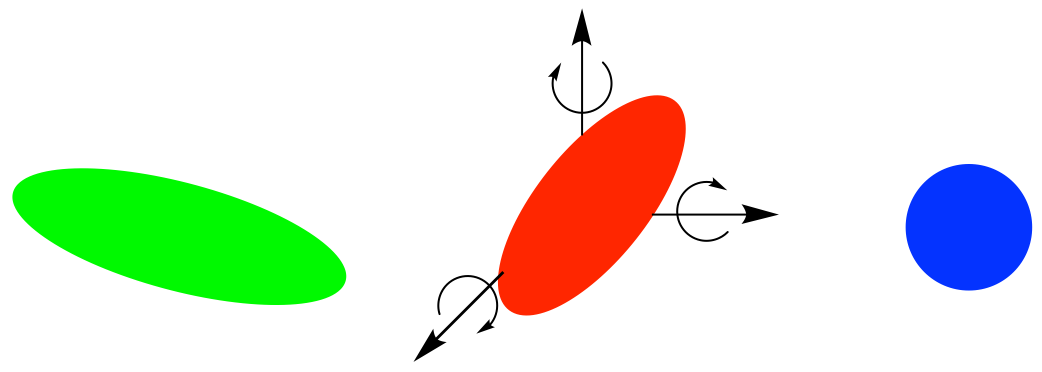
The rotation angles can be specified using the keyword “ISOSEARCH_LIGAND_ROT=(l,m,n)” with the default setting being 60 degrees (l=m=n=6). When the keyword “ISOSEARCH_LIGAND_ROT=(8,8,8)” is used, the rotation angles are set to 45 degrees, respectively.
[Orientation Search of Phenol in α-Cyclodextrin]
As shown in the figure below, structural data (aCD_phenol.mol) for a phenol molecule located near the inside of α-cyclodextrin is available in the Sample_Files/CONFLEX/in-situ_search in the folder where CONFLEX is installed, so copy this and open it in the CONFLEX Interface. You can omit hydrogen atoms as shown in the figure by selecting [Hydrogens] in [Show/Hyde] from View menu of CONFLEX Interface.
Here, we set and run the orientation search of phenol molecule.
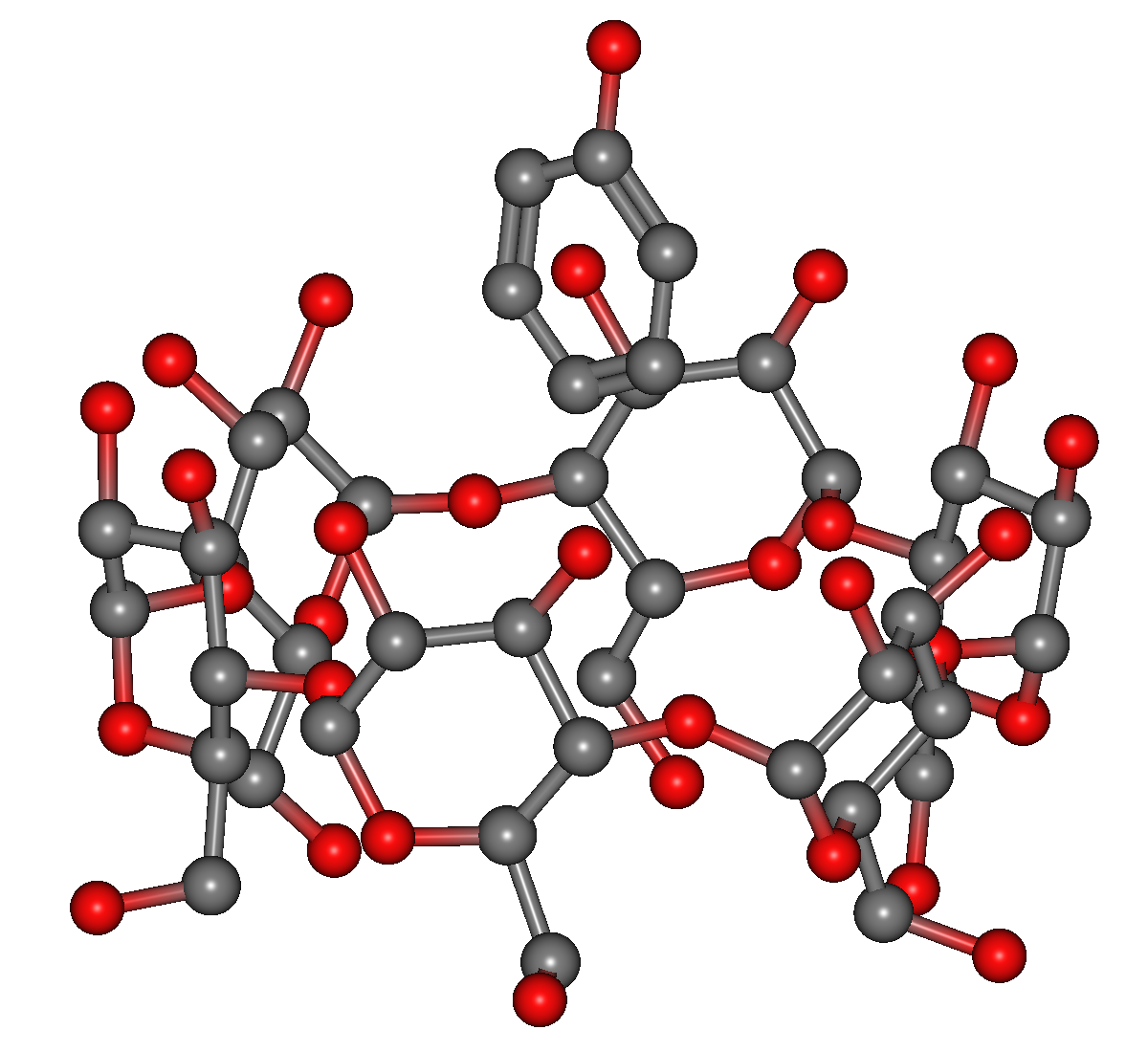
Input data of α-cyclodextrin and phenol (aCD_phenol.mol)
aCD_phenol.mol
139145 0 0 0 1 V2000
-0.9900 -5.1813 1.7326 C 0 0 0 0 0
0.4703 -5.2557 2.1169 C 0 0 0 0 0
1.3126 -4.4420 1.1593 C 0 0 0 0 0
1.0559 -4.8370 -0.2876 C 0 0 0 0 0
-0.4459 -4.8668 -0.5733 C 0 0 0 0 0
...
...
3.3185 3.0495 3.8277 H 0 0 0 0 0
1 2 1 0 0 0
1 10 1 6 0 0
1 20 1 0 0 0
...
...
131137 1 6 0 0
132138 1 0 0 0
133139 1 0 0 0
M END
[Execution form Interface]
Select [CONFLEX] in Calculation menu, and click in the calculation setting dialog that appears. When the detail setting dialog opens, select [Host Ligand Search] in the pull-down menu of [Calculation Type:] in the [General Settings] dialog.
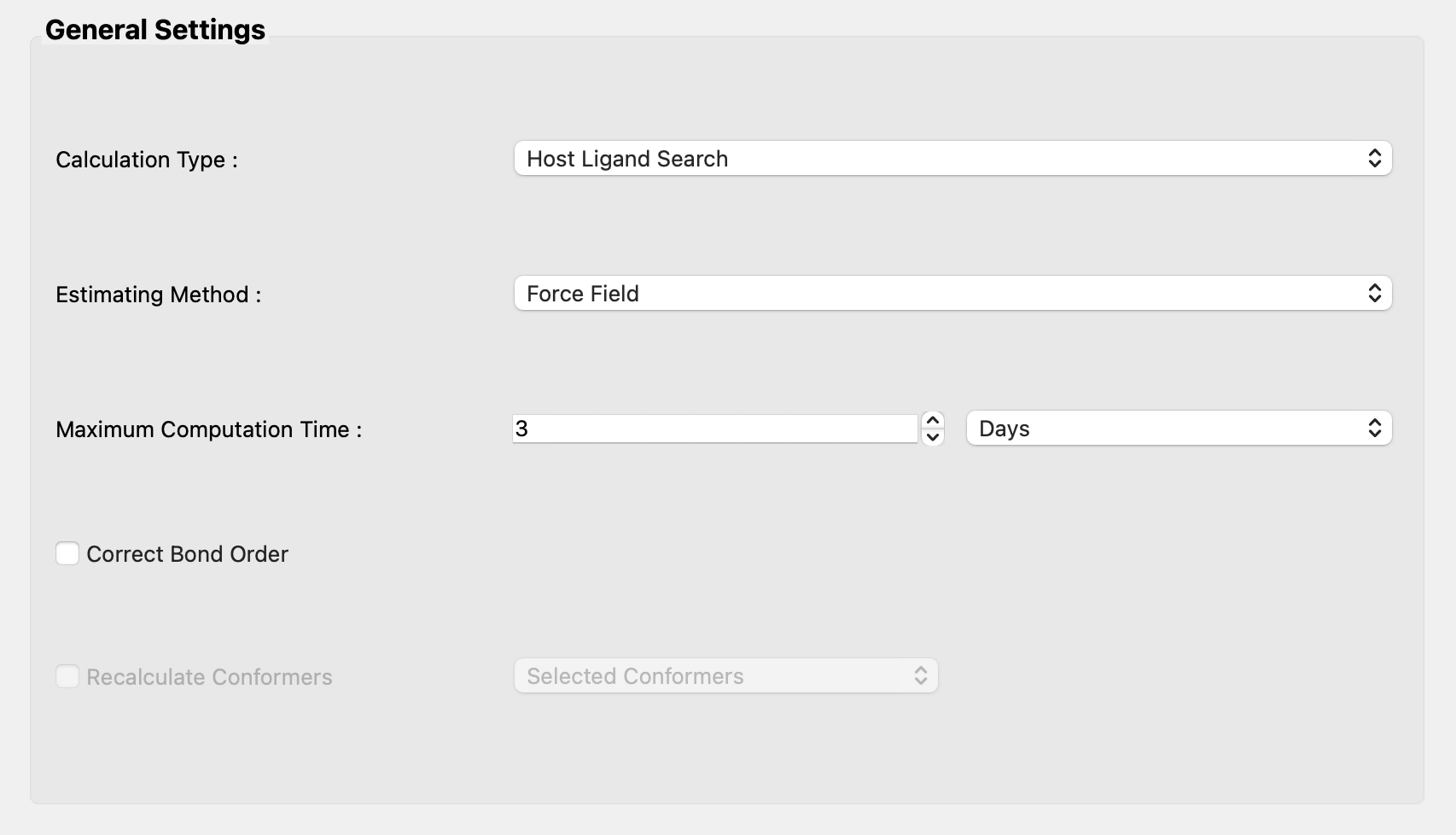
Next, uncheck [Host settings:] in the [Host Ligand Search] dialog.
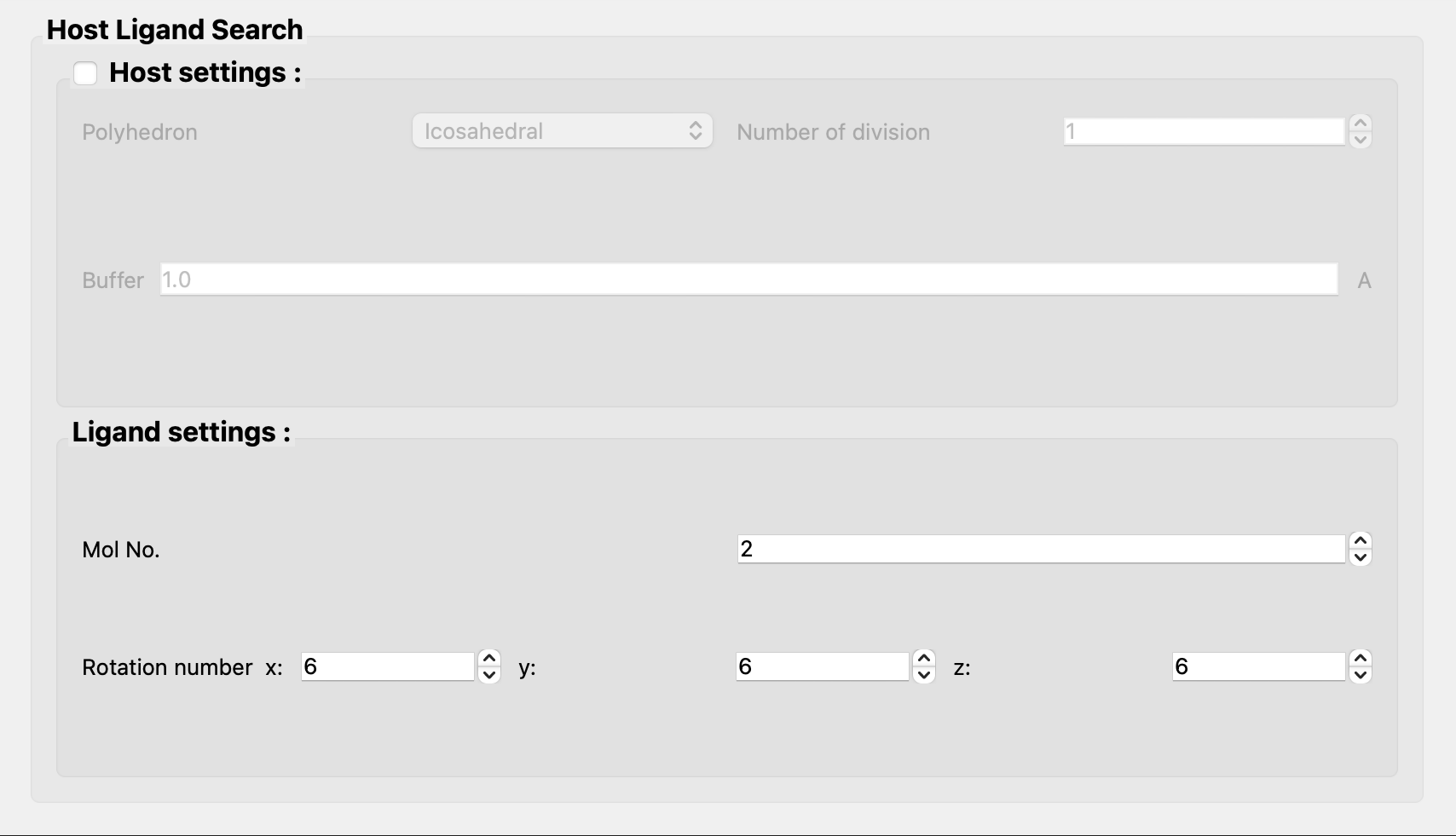
Finally, click and add [NOSYMMETRY] to the dialog that appears. This will prevent structural transformation to determine symmetry.
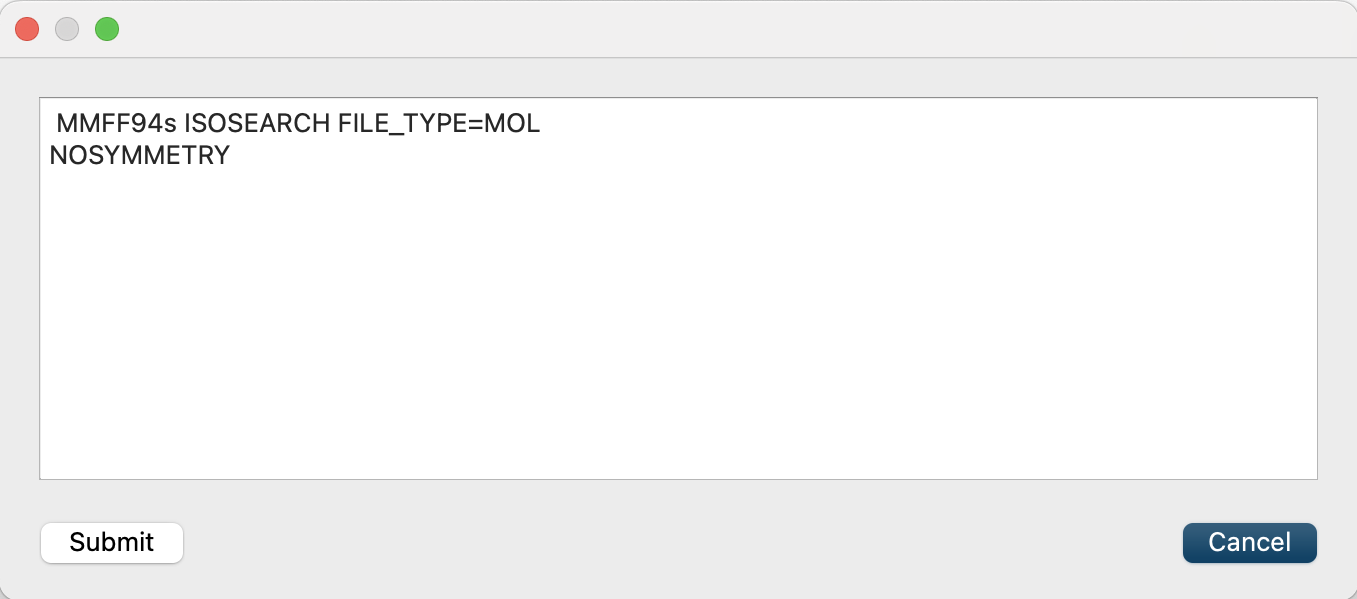
When the calculation settings are complete, click . The orientation search for phenol will run.
[Execution from command line]
The calculation settings are defined by describing keywords in the aCD_phenol.ini file as below. In-Situ Orientation search is performed by including the [ISOSEARCH] keyword.
aCD_phenol.ini
ISOSEARCH NOSYMMETRY
Save aCD_phenol.mol and aCD_phenol.ini files in the same folder, and execute below command.
C:\CONFLEX\bin\conflex-10a.exe -par C:\CONFLEX\par aCD_phenolenter
The above command is for Windows OS. For the other OS, please refer to [How to execute CONFLEX].
Computational results
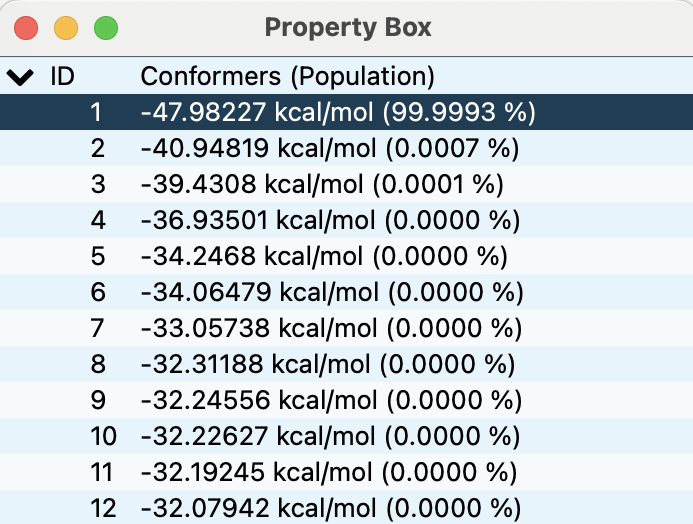
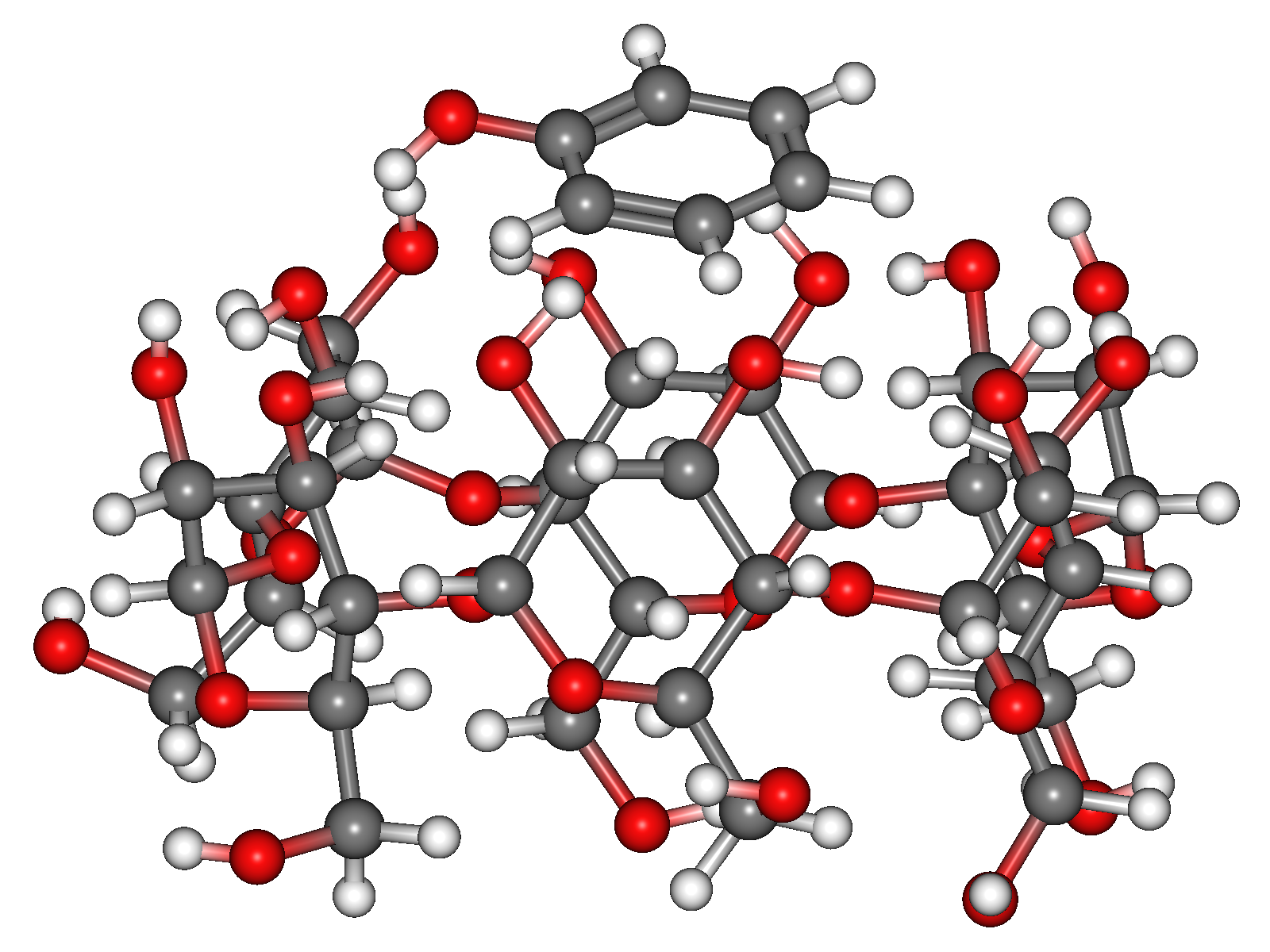
From this calculation, we obtain 56 energy-minimum structures. The most stable structure is shown in the below figure.
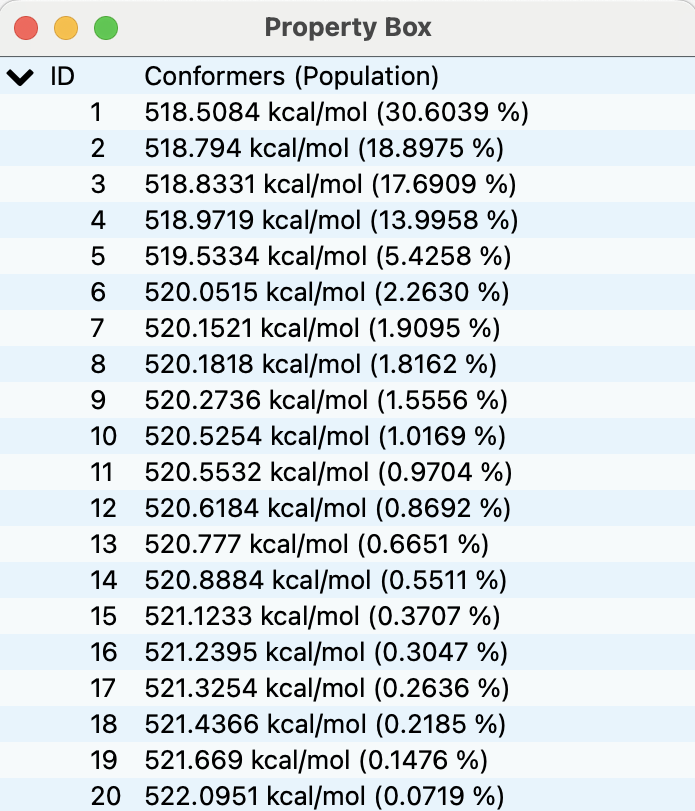
The energy list is shown in the Property Box (below figure) as in the conformation search calculation.
About how to visualize the structures, please refer to [Visualization of calculation results].
[Orientation search of acetic acid between two other acetic acid molecules]
As shown in the figure below, structural data (acetic_acid_trimer.mol) for 3 acetic acid molecules arranged in parallel at 5Å intervals (Z-axis direction) is available in the Sample_Files/CONFLEX/in-situ_search in the folder where CONFLEX is installed, so copy this and open it in the CONFLEX Interface.
Here, we set and run the orientation search of central molecule with fixing the molecules at both ends.
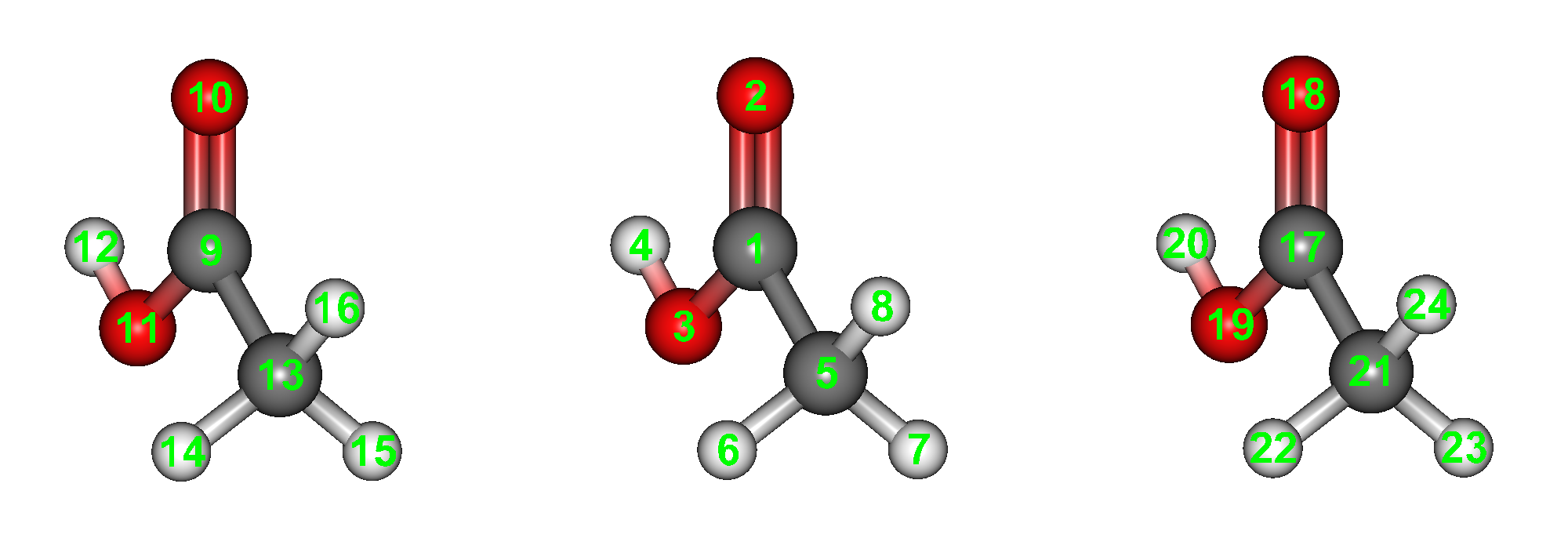
Input data of acetic acid trimer (acetic_acid_trimer.mol)
acetic_acid_trimer.mol
24 21 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0.9628 -0.5511 0.0000 C 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2.1931 -0.5511 0.0000 O 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0.3335 0.6511 0.0000 O 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
...
...
0.5138 -2.6519 -5.0000 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 2 2 0 0 0 0
1 3 1 0 0 0 0
1 5 1 0 0 0 0
...
...
21 24 1 0 0 0 0
M END
[Execution from Interface]
Select [CONFLEX] in Calculation menu, and click in the calculation setting dialog that appears. When the detail setting dialog opens, select [Host Ligand Search] in the pull-down menu of [Calculation Type:] in the [General Settings] dialog.

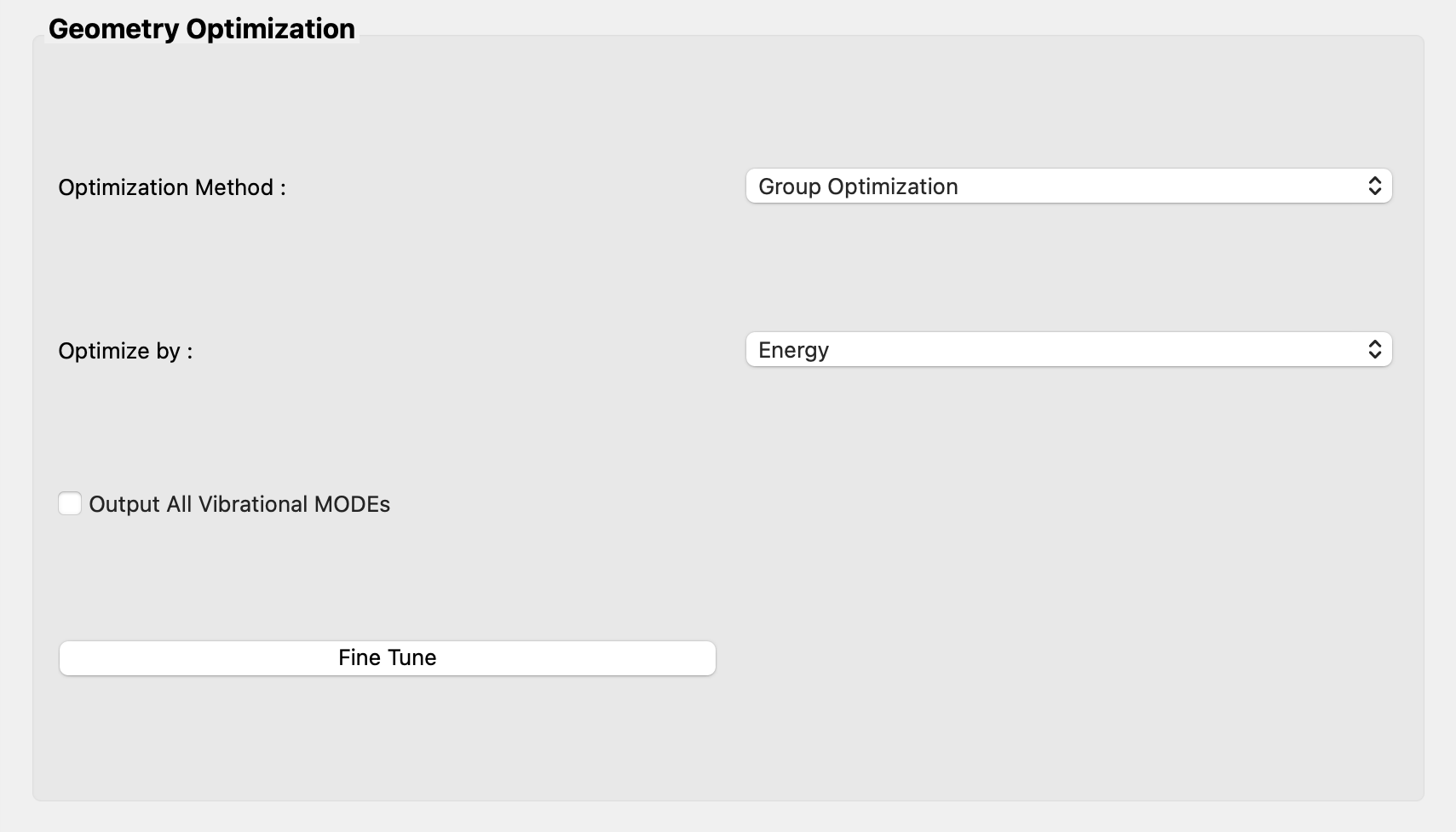
Next, select [Group Optimization] in the pull-down menu of [Optimization Method :] in the [Geometry Optimization] dialog.
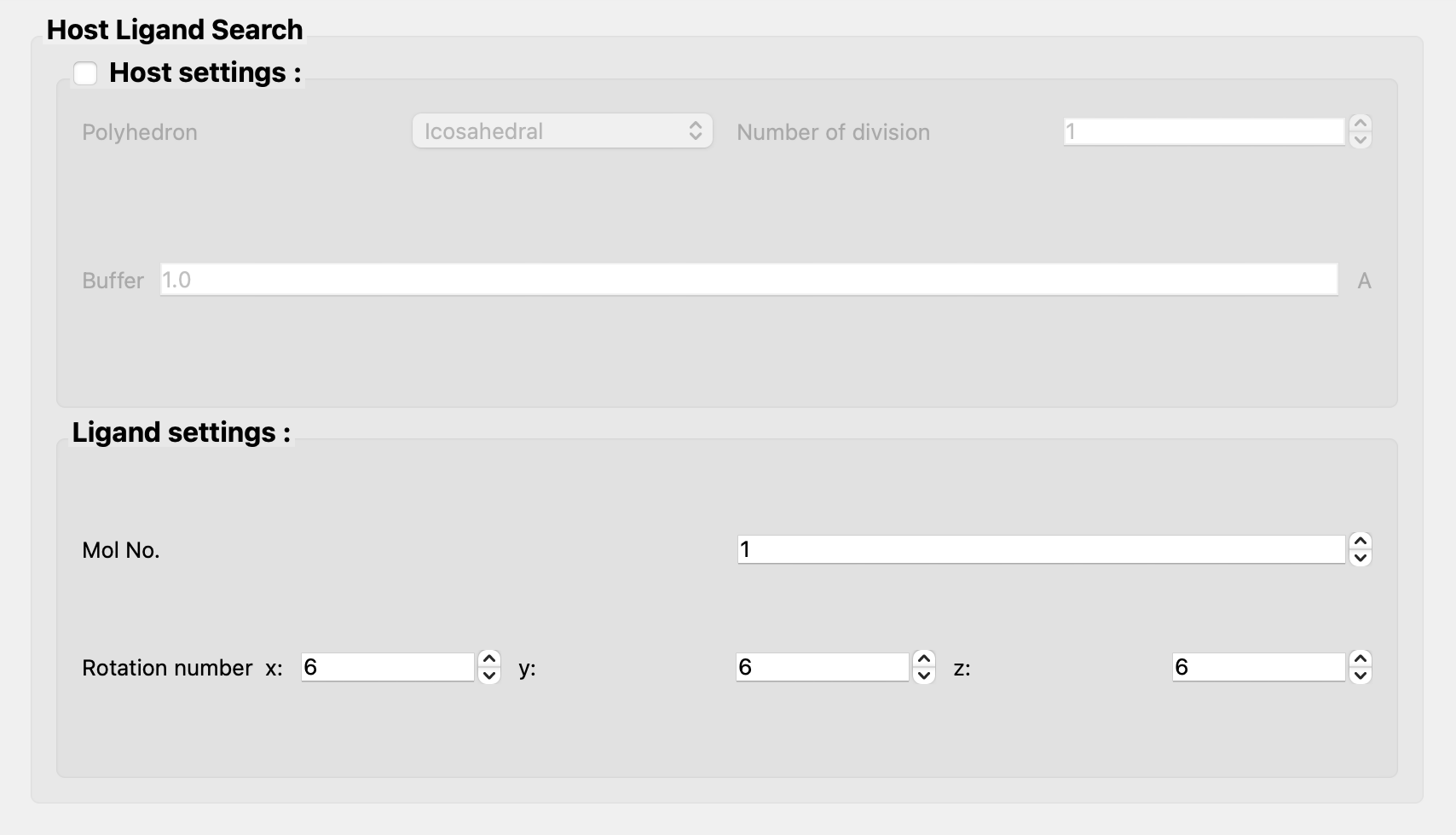
Next, uncheck [Host settings:] and set "1" at [Mol No.] of [Ligand settings:] in the [Host Ligand Search] dialog.
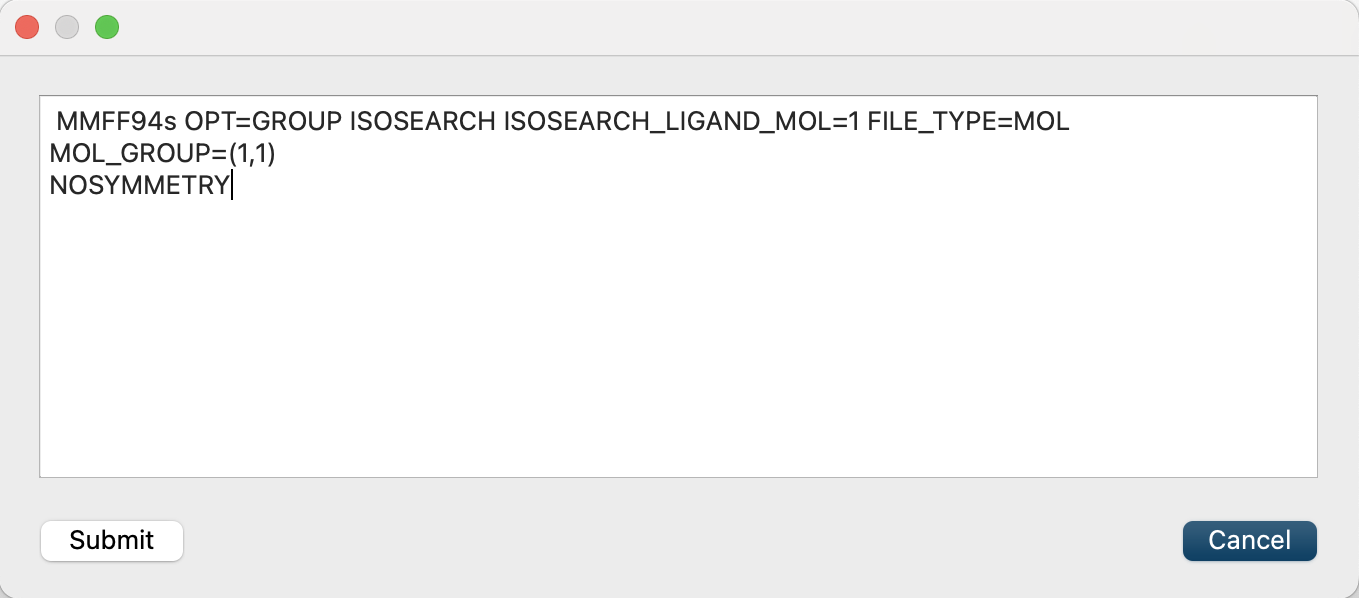
Finally, click and add [MOL_GROUP=(1,1)] and [NOSYMMETRY] to the dialog that appears. This will optimize only center molecule and prevent structural transformation to determine symmetry.
[Execution from command line]
The calculation settings are defined by describing keywords in the acetic_acid_trimer.ini file as below.
acetic_acid_trimer.ini
ISOSEARCH ISOSEARCH_LIGAND_MOL=1 OPT=GROUP MOL_GROUP=(1,1) NOSYMMETRY
In-Situ Orientation search is performed by including the [ISOSEARCH] keyword, and the central molecule is the target of orientation search by including [ISOSEARCH_LIGAND_MOL=1]. In addition, geometry optimization is performed only on the central molecule by including [OPT=GROUP] and [MOL_GROUP=(1,1)].
About a geometry optimization with constraints, please refer to [Constraint by molecular object method].
Save acetic_acid_trimer.mol and acetic_acid_trimer.ini files in the same folder, and execute below command.
C:\CONFLEX\bin\conflex-10a.exe -par C:\CONFLEX\par acetic_acid_trimerenter
The above command is for Windows OS. For the other OS, please refer to [How to execute CONFLEX].
Computational results
From this calculation, we obtain 12 optimized structures. Molecular window will be divided into 3 rows and 4 columns by setting [Columns:] to 4 and [Rows:] to 3 at the top of window, and all structures can be displayed as shown below.
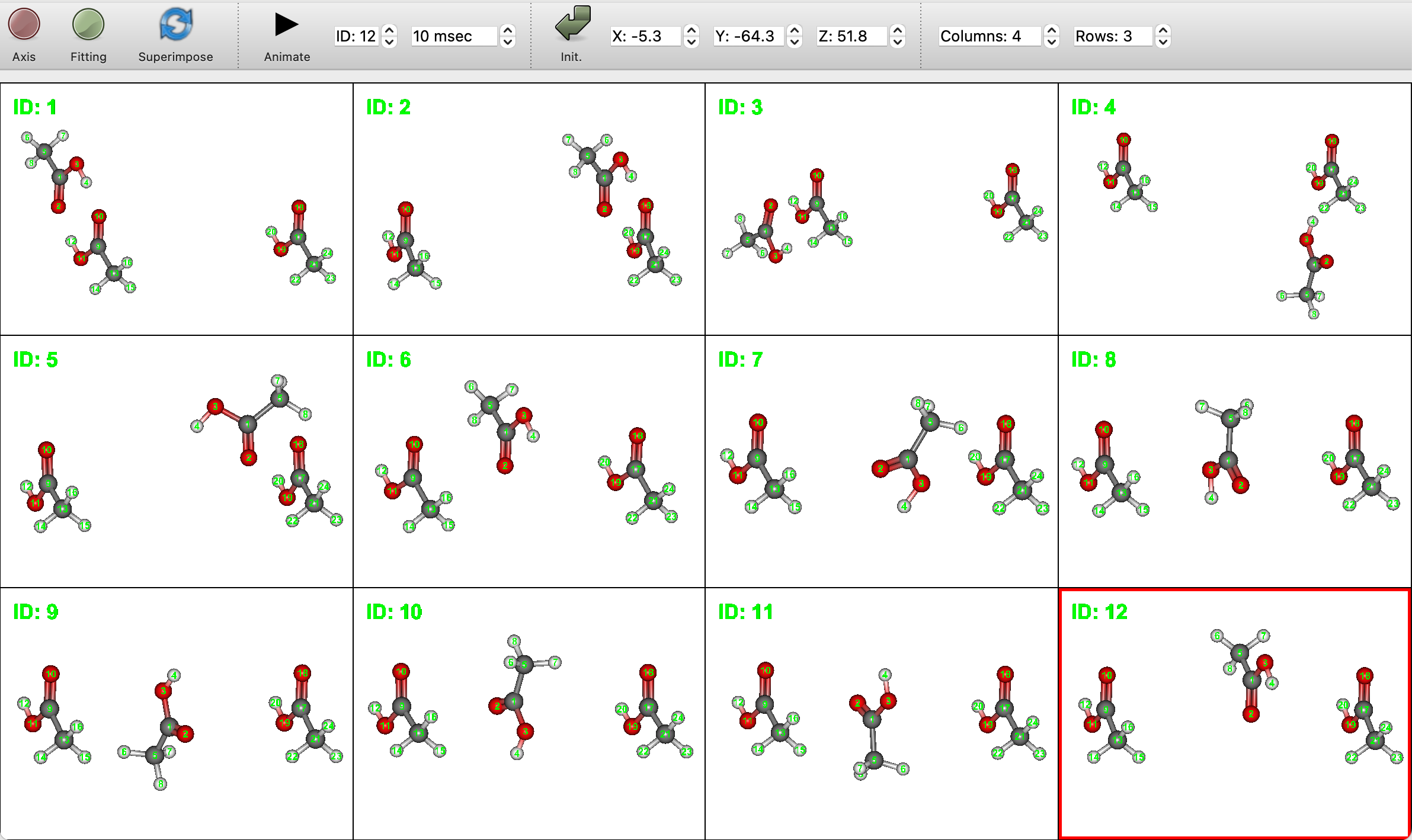
The energy list is shown in the Property Box (below figure) as in the conformation search calculation.
About how to visualize the structures, please refer to [Visualization of calculation results].